I.Introduction
Substrate wetting agents are surfactants that can make solid materials more easily wetted by water by reducing their surface energy. A substance that makes solid materials more easily wetted by water. By reducing its surface or interfacial tension, water can spread on the surface of the solid material or penetrate its surface, thereby moistening the solid material.
Water-based coatings use water as the medium. Water-based coating additives are an essential part of the preparation and application process of water-based coatings. Water-based coating additives mainly include substrate-wetting agents, defoaming agents, leveling agents, dispersants, Thickeners, multifunctional additives, film-forming additives, fungicides, etc. The following first introduces the substrate-wetting agent.
Both the surface of the substrate and the coating formulation can affect wetting. In principle, if the surface tension of the liquid is lower than the free surface energy of the substrate, then the surface of the solid can be well-wetted. Among them, low surface energy substrates include polyethylene and polypropylene. High surface energy substrates include metals, metal oxides, and glass.
Cleaning metal substrates can remove grease on the surface and increase surface energy. Corona treatment of plastic surfaces has a similar effect, creating a more capable surface area through oxidation. The material itself and its surface structure is an influencing factors and can in some cases improve wettability. The most common way to improve wetting is to add a substrate wetting agent to the liquid. These surface-active substances can preferentially adhere to the interface, and their concentration at the interface is higher than the concentration in the bulk.
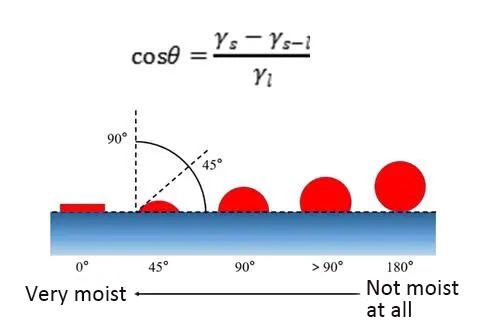
Substrate wetting refers to the process by which gases on the surface of the substrate are replaced by liquid paint. This process is critical to the successful application of paint. Wetting can be described by the contact angle θ. The contact angle depends on the surface energy and surface tension. Young’s equation can express the relationship:
Ys: Surface energy of the substrate
Ys-l: Interfacial tension between coating and substrate
Yl: Surface tension of paint liquid surface
If the contact angle θ <90°, the coating can wet the substrate. The smaller θ is, the better the wetting and spreading is.
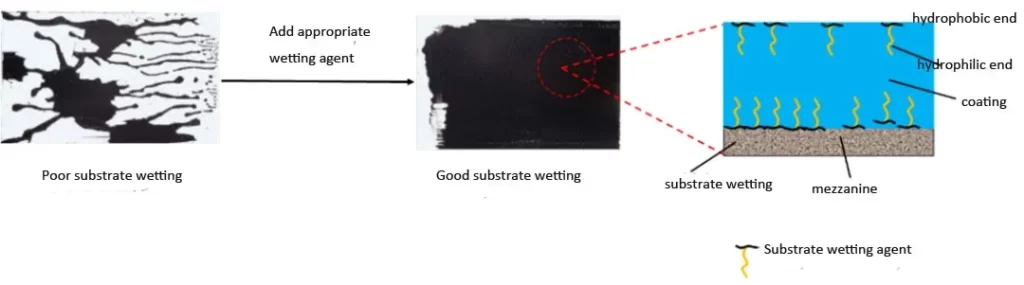
The substrate-wetting agent is composed of a hydrophilic end and a hydrophobic end and has a small molecular weight. One part acts on the liquid-solid interface to form an interlayer, making it easier for the liquid to spread; the other part acts on the gas-liquid interface to reduce the surface tension of the liquid and promote wetting of the substrate. Its mechanism of action is shown in the figure below:
II.Types of substrate wetting agents for water-based coatings
There are four main categories:
1. The polyether-modified dimethylsiloxane base material wetting agent greatly reduces the static surface tension of the system, has excellent wetting and anti-crater properties, and does not increase surface smoothness and does not affect the interlayer Adhesion, but may have the disadvantage of foam stabilization. Such substrate wetting agents include: Tego Wet 270, Tego Wet 280, BYK 346, BYK 349, BYK 3481, etc.
2. The organic twin polyether-modified silicone wetting agent contains at least two hydrophobic segments, two hydrophilic segments, and a flexible bridging group or bridging group. This molecular structure can strongly reduce the static surface tension of the system, reduce the dynamic surface tension of the system to a certain extent, improve the penetration, wetting, and spreading of extremely low energy surfaces, and has excellent anti-crater properties; it also has certain defoaming properties. Such products mainly include : Tego Twin 4100, Tego Twin 4200, etc.
3. The acetylenic glycol twin surfactant type wetting agent has the molecular structure of ethoxyacetylenic glycol surfactant. Its spacer group generally connects amphiphilic molecules and dihydrophobic molecules. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) ratio ” The amount of “monad” surfactant is lower, which means that the same or even better wetting effect as “monad” can be achieved with a smaller amount.
However, since this type of surfactant does not contain silicon, its ability to reduce static surface tension is not very strong, and its wetting and spreading are relatively weak. However, it can strongly reduce dynamic surface tension, has good permeability to the substrate, and has excellent defoaming and antifoaming performance without affecting interlayer adhesion. Such products mainly include Surfynol 440, surfynol 104E, Surfynol AD01, BYK-DYNWET 800, etc.
Note: Due to its serious side effects, fluorocarbon surfactants are currently rarely used in the actual production and application of water-based coatings.
III. Applications in Different Industries
This section would detail how substrate wetting agents are used in different industries:
- Agriculture: For improving water infiltration in soil, aiding in nutrient uptake.
- Manufacturing: In the production of paints and coatings, they ensure uniform application.
- Textiles: Used in dyeing processes to ensure even color distribution.
- Other Industries: Their application in areas like pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and more.
IV.Advantages and Benefits
Improved Efficiency: Wetting agents can significantly improve the efficiency of processes like irrigation and painting.
Cost Savings: By enhancing the effectiveness of other products (like fertilizers and paints), wetting agents can lead to cost savings.
Environmental Impact: Modern wetting agents are designed to be more environmentally friendly, reducing potential negative impacts.